Introduction
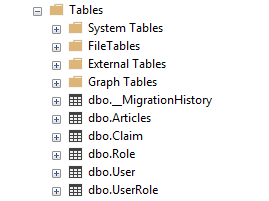
In the previous section, we created an ASP.NET Identity database by using EF Code-First approach.
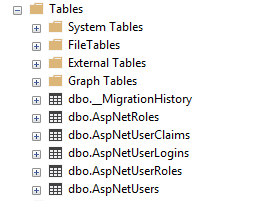
In this section, we will see how to customize the above ASP.NET Identity tables.
Add a column in the AspNetUsers table
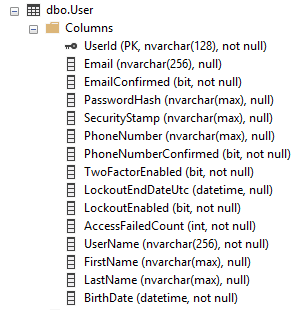
Here are the default columns of the AspNetUsers table :
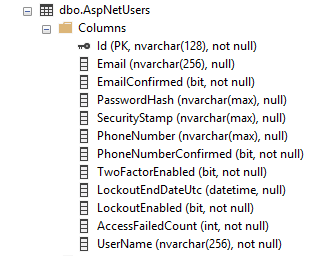
In order to add a column in the AspNetUsers table, go to the IdentityModels.cs file and add the
corresponding property in the ApplicationUser class.
public class ApplicationUser : IdentityUser
{
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public DateTime BirthDate { get; set; }
/*...*/
}
In preceding code, we added 3 properties in the ApplicationUser class (first name, last name and birth date of the user). This will translate into the following :
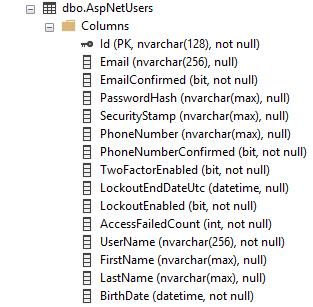
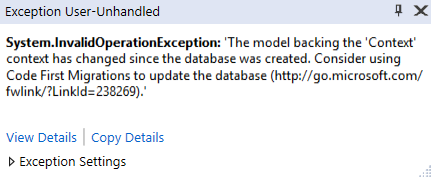
Note : You have to enable the code-first migrations in your project to be able to update the database schema. Otherwise, you will get the following error message :
Configure relationships
You can configure relationships between ASP.NET Identity entities and your own entities by using EF Fluent API
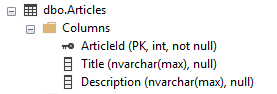
Let's assume we want to configure a One-to-Many relationship between the AspNetUsers table and
the following Articles table :
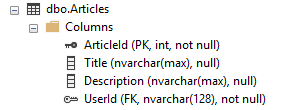
In order to establish this relationship where a user can publish multiple articles :
-
Include a collection navigation property of type
ICollection<Article>in the ApplicationUser class. -
Include a navigation property of type
ApplicationUserin the Article class with theUserIdproperty as a foreign key. - In the Context class, override the OnModelCreating method and use the Fluent API methods in order to configure the One-to-Many relationship between the two entities, as shown below.
public class ApplicationUser : IdentityUser
{
public ApplicationUser() {
articles = new List<Article>();
}
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public DateTime BirthDate { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Article> articles { get; set; }
/*...*/
}
public class Article
{
public int ArticleId { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public string UserId { get; set; }
public virtual ApplicationUser user { get; set; }
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
modelBuilder.Entity<ApplicationUser>()
.HasMany(u => u.articles)
.WithRequired(a => a.user)
.HasForeignKey(a => a.UserId);
}
This will result in the creation of a foreign key in the Articles table that refers to the primary kay in
the AspNetUsers table.
Rename the AspNetUsers table
In order to rename an ASP.NET Identity table and give it a more relevant name, we use the ToTable method.
modelBuilder.Entity<ApplicationUser>().ToTable("User");
This will change the name of the AspNetUsers table to User.
We can use the same method to rename all ASP.NET Identity tables.
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
modelBuilder.Entity<ApplicationUser>().ToTable("User");
modelBuilder.Entity<IdentityRole>().ToTable("Role");
modelBuilder.Entity<IdentityUserRole>().ToTable("UserRole");
modelBuilder.Entity<IdentityUserClaim>().ToTable("Claim");
modelBuilder.Entity<IdentityUserLogin>().ToTable("Login");
}
And this will be the result :
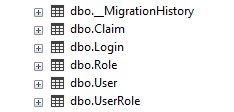
Rename the Id column of the AspNetUsers table
In order to change the column name of an ASP.NET Identity table, we use the HasColumnName method.
modelBuilder.Entity<ApplicationUser>().Property(u => u.Id).HasColumnName("UserId");
In preceding code, we change the name of the Id column in the AspNetUsers table to UserId.
Remove the AspNetUserLogins table
First, go to the Migrations > Configuration.cs file and set the
AutomaticMigrationDataLossAllowed property to true in the constructor of the class.
public Configuration()
{
AutomaticMigrationsEnabled = true;
AutomaticMigrationDataLossAllowed = true;
ContextKey = "AspNetIdentityApp.Models.Context";
}
This will allow the data loss during the automatic migration. If you don't set this property to true, you
won't be able to remove the AspNetUserLogins table and you will get the following error message :
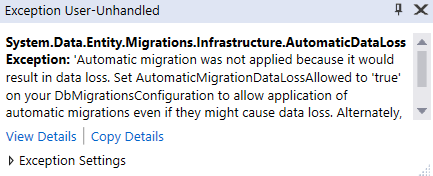
In order to remove the AspNetUserLogins table, we need to override the default ASP.NET Identity entities configuration.
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<ApplicationUser>().ToTable("User");
modelBuilder.Entity<ApplicationUser>().HasMany(u => u.Roles).WithRequired().HasForeignKey(ur => ur.UserId);
modelBuilder.Entity<ApplicationUser>().HasMany(u => u.Claims).WithRequired().HasForeignKey(uc => uc.UserId);
modelBuilder.Entity<ApplicationUser>().Property(u => u.UserName)
.IsRequired()
.HasMaxLength(256)
.HasColumnAnnotation("Index", new IndexAnnotation(new IndexAttribute("UserNameIndex") { IsUnique = true }));
modelBuilder.Entity<ApplicationUser>().Property(u => u.Email).HasMaxLength(256);
modelBuilder.Entity<ApplicationUser>()
.HasMany(u => u.articles)
.WithRequired(a => a.user)
.HasForeignKey(a => a.UserId);
modelBuilder.Entity<IdentityUserRole>()
.HasKey(r => new { r.UserId, r.RoleId })
.ToTable("UserRole");
modelBuilder.Entity<IdentityUserClaim>().ToTable("Claim");
var role = modelBuilder.Entity<IdentityRole>()
.ToTable("Role");
role.Property(r => r.Name)
.IsRequired()
.HasMaxLength(256)
.HasColumnAnnotation("Index", new IndexAnnotation(new IndexAttribute("RoleNameIndex") { IsUnique = true }));
role.HasMany(r => r.Users).WithRequired().HasForeignKey(ur => ur.RoleId);
modelBuilder.Entity<ApplicationUser>().Ignore(u => u.Logins);
modelBuilder.Ignore<IdentityUserLogin>();
}
Besides the default model configuration, we added these two lines :
modelBuilder.Entity<ApplicationUser>().Ignore(u => u.Logins);
modelBuilder.Ignore<IdentityUserLogin>();
We used the Ignore method on the EntityTypeConfiguration<ApplicationUser>
object in order to exclude the Logins property from the model. We used the same method on the modelBuilder
object to exclude the IdentityUserLogin entity from the model. This will result in the removal of
the AspNetUserLogins table.